
Technological advancements in agriculture enable farmers to meet the ever-increasing demand through low-cost and efficient methods. To aid this, precision agriculture startups simplify farming management by measuring, responding, and observing the variability of crops and fields through precision agriculture equipment and software solutions. This article provides an overview of the top 8 global precision agriculture trends based on the analysis of 589 Agri-Tech startups and scaleups by startus-insights.com/. The application of these trends allows farmers to collect real-time data on the crop fields and increase product quality among others.
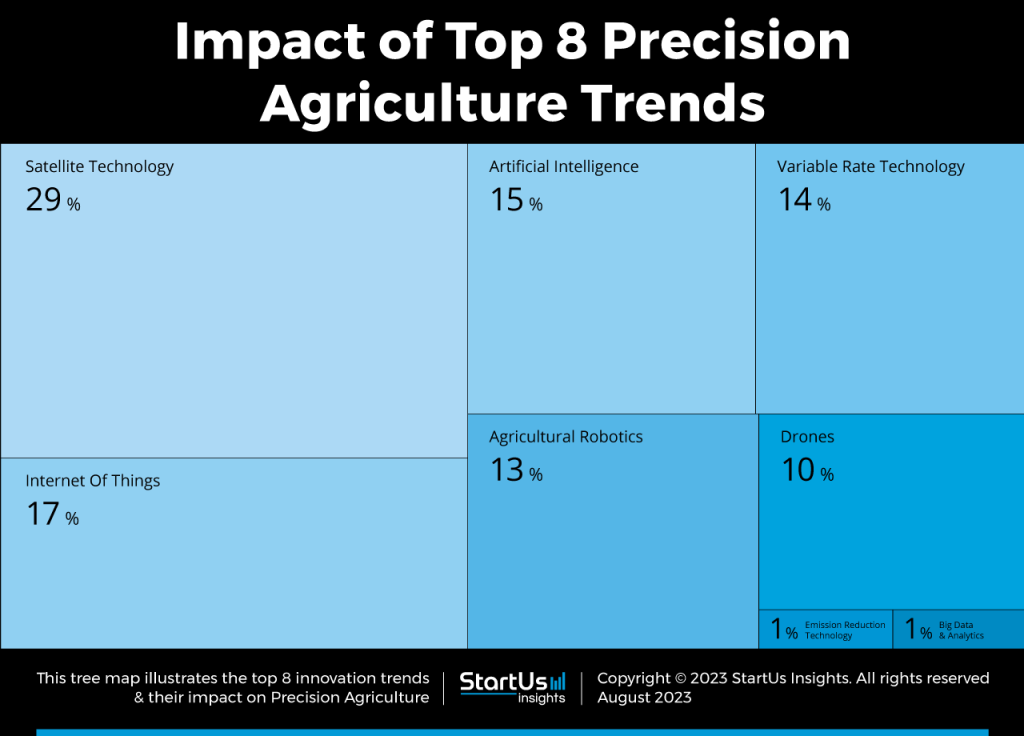
Based on this report, The most impactful area is Satellite Technology with 29% of impact. Startups and scaleups are developing satellite technology solutions powered by Global Positioning Systems (GPS) tracking and geographical information systems (GIS) mapping methods to collect data in real time. Moreover, IoT solutions are in demand as data collection plays an essential role in boosting productivity and efficiency.
In addition, AI, variable rate technology, robotics, and drone solutions cover a large portion of this trend. Since site-specific management is an important topic of AgriTech, soil mapping through big data provides precise information about farmlands. Lastly, emission reduction technologies help farmers control carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions by processing large datasets.
1. Satellite Technology
Variability and quality of data are the main challenges preventing the further implementation of sustainable agriculture practices. Satellite technology in agriculture helps farmers analyze large areas of their farms in a short period of time and in real-time.
Moreover, it allows farmers to react immediately to localized issues like fertilization and irrigation. Technologies such as GIS and GPS further enable farmers to determine the topography, heterogeneity, and yield estimation of crops, as well as for livestock tracking.
Data collection is becoming an integral part of the agricultural process. To decide which types of pesticides and fertilizers should be used for reaching optimal efficiency, monitoring weather conditions, taking control of production processes, and lowering production risks, farmers turn to IoT solutions.
The use of IoT sensors, such as RFID chips, helps farmers optimize all aspects of their work, including crop farming and tracking cattle. Further, the live monitoring of the field data enables farmers to make the best decisions on upcoming production while reducing their environmental impact.
AI enhances the data collected from various sensors to enable precision agriculture and improve harvest quality and accuracy. AI also makes various other aspects of Agtech operations smarter. For example, water management and energy consumption are optimized with AI, which leads to much more accurate decisions taken by the farmers. Machine learning and deep learning techniques are becoming an integral part of agriculture and are utilized in soil and crop monitoring, and agricultural robotics, among others.
One of the most reliable methods of boosting productivity is the application of variable rate technology in precision agriculture. VRT enables the application of water, nutrients, and other factors of production at varying rates across a field. This eliminates the need to make multiple runs across an area or constantly change rate settings on machinery.
Moreover, VRT eliminates the time-consuming agricultural tasks that are done manually while also reducing the chance of human error. Hence, VRT helps farmers boost productivity, increase precision, and improve risk management. Some examples of VRT include fertigation systems, precision pest management, and variable rate application. Precision sprayers and many more.
5. Agricultural Robotics
The increasing demand for food and shortage of labor affects agriculture in all aspects. Agricultural robots assist farmers in solving the above-mentioned challenges. Moreover, agricultural robots are capable of data gathering and analysis to increase crop yields. Additionally, technological advancements in robotics in agriculture allow farmers to assign robots to repetitive and time-consuming tasks.
Applications of robotics in agriculture include automated and assisted steering systems, mobile agricultural robot swarms (MARS), and mechanical swarms, among others. Furthermore, robotics automation in agriculture decreases resource consumption and the chance of human error, leading to cost-efficient production and improved food quality.
6. Drones
Plant health monitoring, pest control, livestock management, aerial surveying, and soil analysis are increasingly performed by drones. Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV), and unmanned ground vehicles (UGV) are utilized in agricultural production to boost the efficiency and quality of products.
Moreover, drones are less prone to human errors and require minimal observation. Further, in conjunction with satellite imagery, drone imagining is incorporated to gain a better understanding of the field potential and soil quality.
Big data & analytics enable farmers to make the right decisions that ultimately improve farm yields. Software solutions provide site- and production-specific insights on rainfall patterns, fertilizer requirements, water cycles, and more. Further, the implementation of big data and analytics makes agricultural production more proficient, productive, and well-regulated while preserving the environment and climate.
Data analytics also assist farmers in real-time plant health monitoring, actionable insights for upcoming yields, and resource management decisions based on established trends. Furthermore, the digitalization of farming reduces labor-related costs while improving efficiency and providing fast and reliable solutions for upcoming production issues.
8. Emission Reduction Technology
Inefficient agricultural activities that increase greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions challenge the agricultural industry more than ever. In this regard, digital technologies in farming reduce emissions through the implementation of carbon capture, utilization, and storage solutions.
In addition, carbon sequestration maps and data analysis platforms have the potential to reduce agricultural inputs by implementing site-specific applications. Emission reduction in agriculture enables farmers to better target inputs to the spatial needs of the fields which results in lower greenhouse gas emissions.
The top 8 precision farming technology trends bring innovative solutions to the agriculture sector to improve productivity, sustainability, and efficiency. The development of satellite and 3D mapping solutions revolutionizes agriculture by making farmers react as quickly as possible to possible negative changes in farms and cattle.
At the same time, environmental protection is becoming a priority for them while using emission reduction solutions to limit carbon emissions into the atmosphere, while also improving the quality of the soil.
The Precision Agriculture Trends & Startups outlined in this report only scratch the surface of trends that we identified during our data-driven innovation & startup scouting process. Among others, emissions reduction, soil remediation, & field analytics solutions will transform the sector and shape the future trends in precision agriculture.
Copyright © 2024, Cropinno Inc.